In SE Ranking’s new analysis, something interesting was examined: What factors influence whether ChatGPT cites a website?
The results are not only interesting for SEO professionals – they even contradict conventional SEO wisdom in some respects and challenge decades of SEO best practices. The study systematically analyzed 129,000 unique domains across 216,524 pages distributed across 20 different niches to identify correlations between over 100 different factors and citation frequency.
The central finding: The factors that ChatGPT prefers for citations are similar to Google ranking factors – but not entirely. This has significant implications for the future of search engine optimization and AI visibility. While many marketers assume that the same optimization strategies work everywhere, a differentiated and partially surprising picture emerges here.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
ToggleReferring Domains and Link Diversity: The Most Dominant Signal
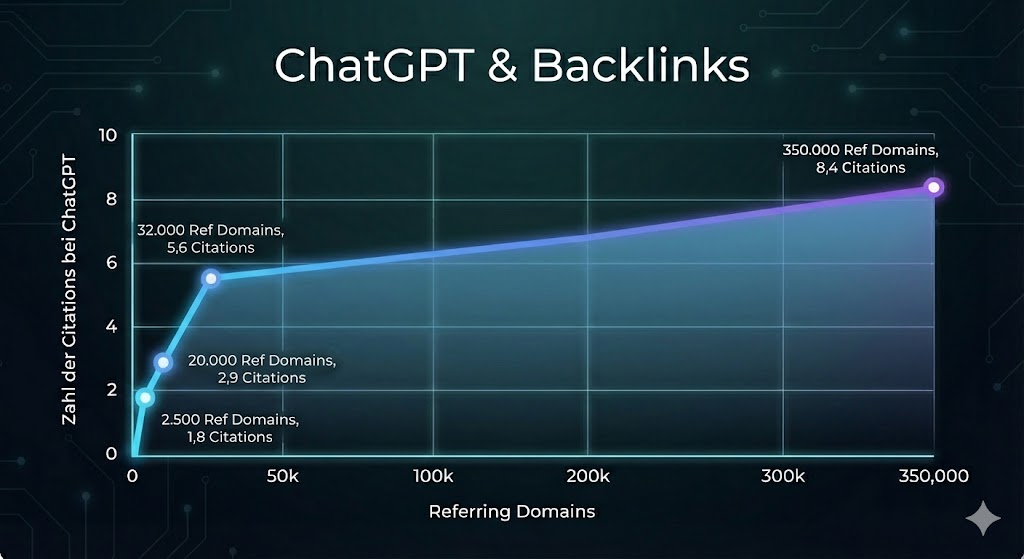
The difference is dramatic and measurable: Websites with up to 2,500 referring domains receive an average of 1.6 to 1.8 citations. Domains with over 350,000 referring domains, however, achieve 8.4 citations – that’s more than a fourfold increase.
A particularly critical threshold lies at 32,000 referring domains: at this point, the citation rate nearly doubles from 2.9 to 5.6.
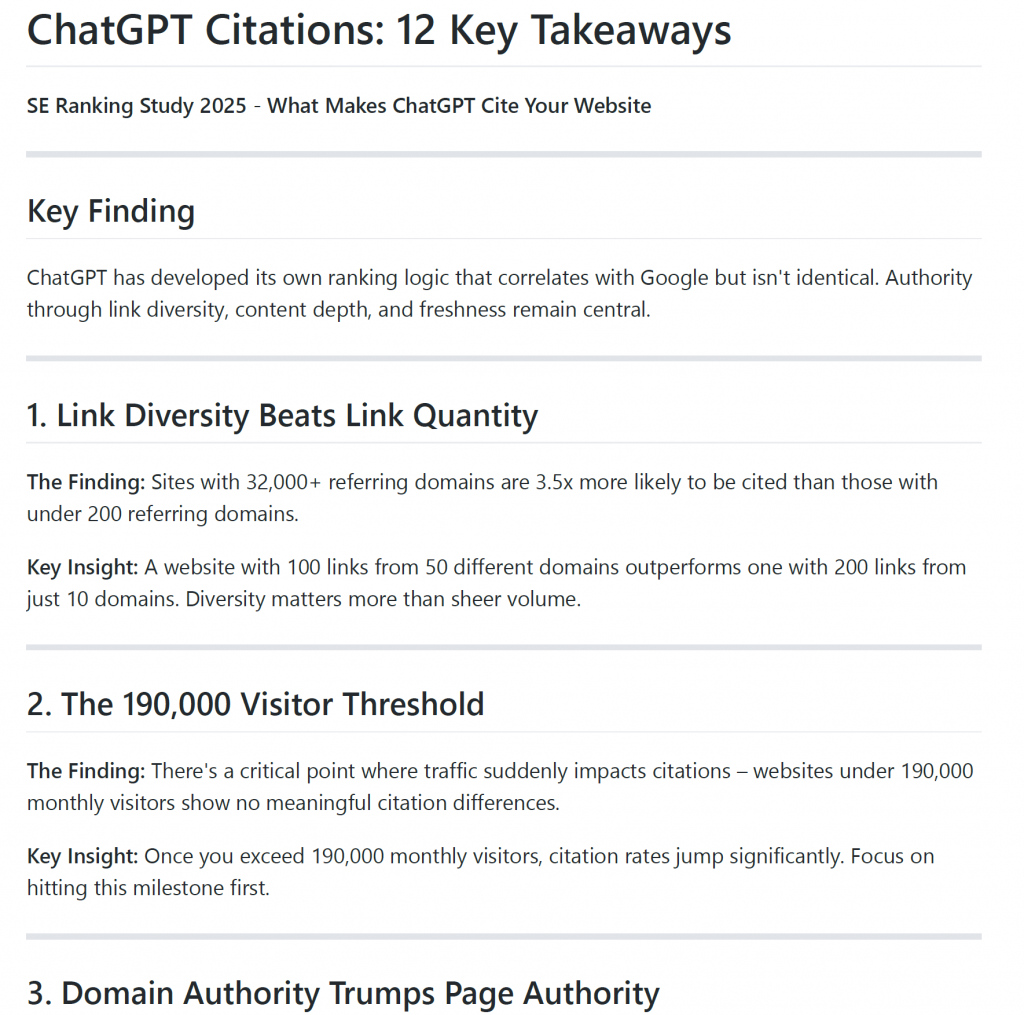
These insights reveal something fundamental: Link diversity is crucial, not the sheer number of links. It’s not about the quantity of links, but about how many different domains link to your website. A website with 100 links from 50 different domains will be significantly preferred by ChatGPT over a website with 200 links from only 10 domains. This means: Quality and diversity beat quantity (no news for SEOs) – a principle that is more stable and future-proof in the long run than aggressive mass linking strategies (Hello, Fiverr fans ;-).
Shameless Plug: If you want to work strategically on link building and build high-quality backlinks from thematically relevant websites with genuine diversity – our link building service focuses precisely on this type of link diversity, with manual research and white-hat link building.
„Sites with over 32K referring domains are 3.5x more likely to be cited by ChatGPT than those with up to 200 referring domains.“
SE Ranking analysis 2025
Traffic and Domain Authority: The Critical Point at 190,000 Visitors
A surprising finding from the study reveals a non-linear pattern that most are unaware of: Domain traffic correlates with ChatGPT citations – but only from a certain critical point onward. Websites under 190,000 monthly visitors show virtually no differences in their citation rate, regardless of whether they receive 20 or 20,000 organic visitors per month – the rates are consistently between 2 and 2.9. Only when websites exceed the critical 190,000-visitor threshold do they see a significant increase in citations. Domains with over 10 million monthly visitors average 8.5 citations.
Particularly relevant is an insight that many overlook: Homepage traffic plays a special role. Websites with at least 7,900 organic visitors to their homepage show the highest citation rates. This suggests that ChatGPT prefers the overall authority and relevance of a domain – not just individual pages or the mere sum of all visits.
Domain Trust Significantly Outperforms Page-Level Authority
ChatGPT appears to weight domain-related authority even more strongly than Google – page-level signals play a lesser role once a certain threshold is reached. A domain with a Domain Trust Score of 97–100 receives an average of 8.4 citations, while one with a score below 43 receives only 1.6 citations – that’s a difference by a factor of five.
Page Trust Scores, on the other hand, show an interesting plateau-like behavior: Every page with a Page Trust Score of 28 or higher receives approximately the same average citation rate of about 8.3 citations. This clearly shows that ChatGPT places less value on individual page metrics than on the overall competence of the domain.
A surprising side finding of the study deserves special attention: .gov and .edu domains do not automatically outperform commercial websites. Government and educational domains receive an average of 3.2 citations, while websites without such „trusted zone“ designations achieve an average of 4.0 citations. This means: The domain suffix is not decisive; the actual link structure and organic trust building count far more than the domain label.
„Site authority really matters… But page authority doesn’t. ChatGPT cites pages from authoritative domains, but not necessarily the most linked-to pages on those domains.„
Ryan Law, Ahrefs
Content Depth and Optimal Paragraph Structure: The 120-180 Word Rule
Content length correlates measurably with ChatGPT citations, but the relationship is more nuanced than simply „longer is better.“ Articles with over 2,900 words receive an average of 5.1 citations, while articles under 800 words receive only 3.2 citations.
The crucial nuance: Structure is more important than pure length. Pages with optimal paragraph length – between 120 and 180 words between headings – perform best and achieve an average of 4.6 citations. In contrast, pages with very short paragraphs (under 50 words) average only 2.7 citations.
This means that ChatGPT doesn’t simply prefer „more words,“ but well-structured, thoroughly explained content that presents complex concepts appropriately and comprehensibly. This finding is particularly important because it shows that readability and clarity matter as much to AI systems as they do to human readers.
Other content factors that correlate positively with citations are equally relevant and should be deliberately considered: Pages with expert quotes receive 4.1 citations compared to 2.4 for pages without quotes – a significant difference of over 70 percent.
Content with 19 or more statistical data points receives 5.4 citations compared to 2.8 for pages with minimal data – this clearly underscores that ChatGPT prefers and rewards data-driven, well-researched content.
Content freshness emerges as one of the clearer signals: Pages updated within the last three months receive 6 citations, while outdated content receives only 3.6. This signals that continuous optimization and timeliness are as important to AI systems as they are to Google – possibly even more so, since ChatGPT relies on current information.
URL Optimization and Title Tags: A Radical Paradigm Shift
This is perhaps the most counterintuitive finding of the entire study, fundamentally challenging previous SEO wisdom: Keyword-optimized URLs perform worse on ChatGPT than URLs with broader topic relevance.
Pages with low semantic relevance between URL and target keyword (0.00 to 0.57 range) receive an average of 6.4 citations. In contrast, pages with highest semantic relevance (0.84 to 1.00) receive only 2.7 citations – less than half.
The same pattern is evident in title tags: Titles with low keyword matching receive 5.9 citations, while highly keyword-optimized titles receive only 2.8 citations.
This finding can be summarized as follows: ChatGPT prefers URLs that clearly describe the overarching topic rather than URLs rigidly optimized for a single keyword.
This signals a fundamental paradigm shift: While traditional SEO long taught „keyword-rich URLs“ as best practice, ChatGPT clearly prefers clarity and thematic breadth. A URL like /chatgpt-citations-seo-factors/ (thematically broad) thus outperforms one like /chatgpt-citations-ranking/ (keyword-specific). The principle behind this: ChatGPT prefers content that is relevant from multiple search queries, not just from a single keyword variant.
Community Engagement and Social Signals: An Underestimated Channel
Brand mentions on discussion platforms show strong correlation with citations – especially for smaller websites that haven’t yet built massive backlink profiles. Domains with minimal Quora presence (up to 33 mentions) receive an average of 1.7 citations. Domains with massive Quora presence (6.6 million mentions) receive 7.0 citations – a fourfold increase that should not be underestimated.
Reddit shows similar patterns: Domains with over 10 million mentions achieve 7 citations compared to 1.8 for domains with minimal activity. Experts note: Engagement on Quora and Reddit offers a realistic opportunity to build authority, similar to how larger websites do it through massive backlink profiles.
Presence on review platforms like Trustpilot, G2, Capterra, Sitejabber, and Yelp also correlates positively with citations. Domains on multiple review platforms receive 4.6 to 6.3 citations on average, while domains on no platform achieve only 1.8. This shows: External trust signals from various sources – not just backlinks, but also rating and community platforms – are valuable and significant for AI systems.
Technical Performance and the Pitfall of Over-optimization
Page Speed Metrics correlate clearly with citation likelihood – an often underestimated factor for AI visibility. Pages with First Contentful Paint under 0.4 seconds receive an average of 6.7 citations. Slower pages (over 1.13 seconds) receive only 2.1 citations – a difference of over 200 percent. Speed Index shows similar patterns: websites under 1.14 seconds perform consistently well, while those over 2.2 seconds suffer dramatic losses.
A counterintuitive finding deserves special attention: Pages with the fastest Interaction to Next Paint scores (under 0.4 seconds) receive fewer citations (1.6 on average) than those with moderate INP scores (0.8 to 1.0 seconds, averaging 4.5 citations). Experts suspect that extremely fast or static pages may not signal the depth and complexity that ChatGPT seeks in authoritative sources – an important hint that over-optimization can be counterproductive.
What DOESN’T Work and Practical Implications for Your Strategy
The study identified several SEO tactics that correlate minimally or even negatively with citations – an important finding for marketers who want to use their resources optimally:
FAQ schema markup is particularly interesting: Pages with FAQ schema receive an average of 3.6 citations, without FAQ schema 4.2 – a disadvantage instead of an advantage. Experts suspect that FAQs often appear on simpler support pages that would deserve fewer citations.
LLMs.txt files show negligible impact – invest your time elsewhere. Outbound links to highly authoritative pages also show minimal effects on citation rates.
These findings should alert SEO professionals: Not all modern SEO tactics are relevant for AI visibility, and some popular best practices can even be counterproductive.
The fundamental insight is reassuring: If you’re already working on a solid SEO strategy – focused on backlinks and link diversity, traffic generation, fast pages, and continuously updated content – you’re automatically optimizing for ChatGPT citations too.
The systems evaluate authority and content quality similarly, meaning good SEO practice works for both channels. The key is to optimize not just for keywords, but for actual topics and genuine user intent.
For smaller websites without massive backlink profiles, the study offers an alternative path: Community engagement on Reddit and Quora is measurable, relatively actionable, and can demonstrably help build authority while longer-term link-building activities take effect.
Conclusion: The Future of AI Visibility Is More Proven Than Expected
The SE Ranking study shows: AI systems like ChatGPT have developed their own ranking logic that correlates with Google rankings but is not identical. Authority through link diversity, content depth and structure, and freshness remain central – but the emphasis lies on clarity over keyword density, domain authority over page authority, and link diversity over raw link quantity.
For SEO professionals, this means: The days of pure keyword optimization are over. The future lies in holistic authority, structured content, and continuous optimization. Those who combine these factors correctly win not only with Google but also with AI systems that increasingly answer user queries.
This isn’t a new game – it’s a return to better fundamental principles that have always worked. The insight about URLs and titles points to a mindset shift: Write for people and AI systems, not just for keywords (oh yes, nothing new again!).
Structure your content with 120-180 word paragraphs, integrate expert quotes and data, keep your content fresh and update it regularly. This is not only good for rankings, but also for your users and for the authority you build.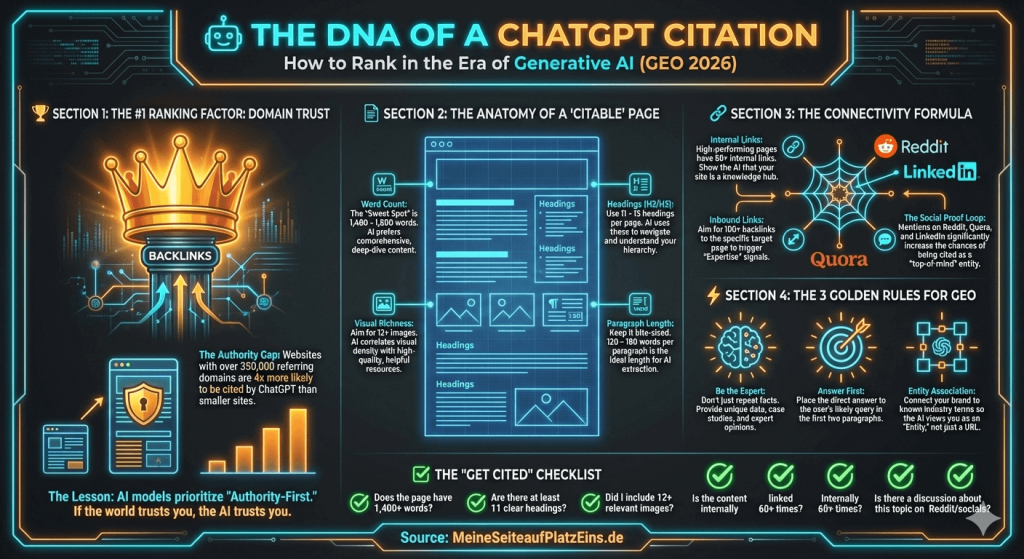
Download Your Free Summary
PDF Preview:
Have you already observed changes in your ChatGPT citations? Which findings surprise you? Your opinion is needed – write in the comments!
Get in touch now for free expert advice!

Boris Alexeev, M.A.
SEO Strategist with 23 Years of Experience
Weitere Artikel
 SEO FAQ 2026 – The Most Important Questions & Answers for Better Google Rankings
SEO FAQ 2026 – The Most Important Questions & Answers for Better Google Rankings SEO Test: Was das ist und warum Sie einen machen sollten (2026)
SEO Test: Was das ist und warum Sie einen machen sollten (2026) SEO Tipps: 12 Fehler, die man beim Linkaufbau vermeiden sollte
SEO Tipps: 12 Fehler, die man beim Linkaufbau vermeiden sollte 3 Gründe, warum Content Marketing immer wichtiger wird
3 Gründe, warum Content Marketing immer wichtiger wird Ist Linkbuilding immer noch von Bedeutung?
Ist Linkbuilding immer noch von Bedeutung? Machen Sie den SEO-Test!
Machen Sie den SEO-Test!












Schreibe einen Kommentar